UNIT 2: Repository Drive/Workspace
What is it?
Google Drive is a file storage and synchronization service that integrates Google Docs, a range of productivity applications that offers editing documents, spreadsheets, presentations, and much more. It is based on the concept of cloud computing, where the users can store files through this service and access them from any computer or other compatible devices, as long as they are connected to the internet. In addition, Google Drive makes several applications available online, without these programs being installed on the computer of the person who uses them.
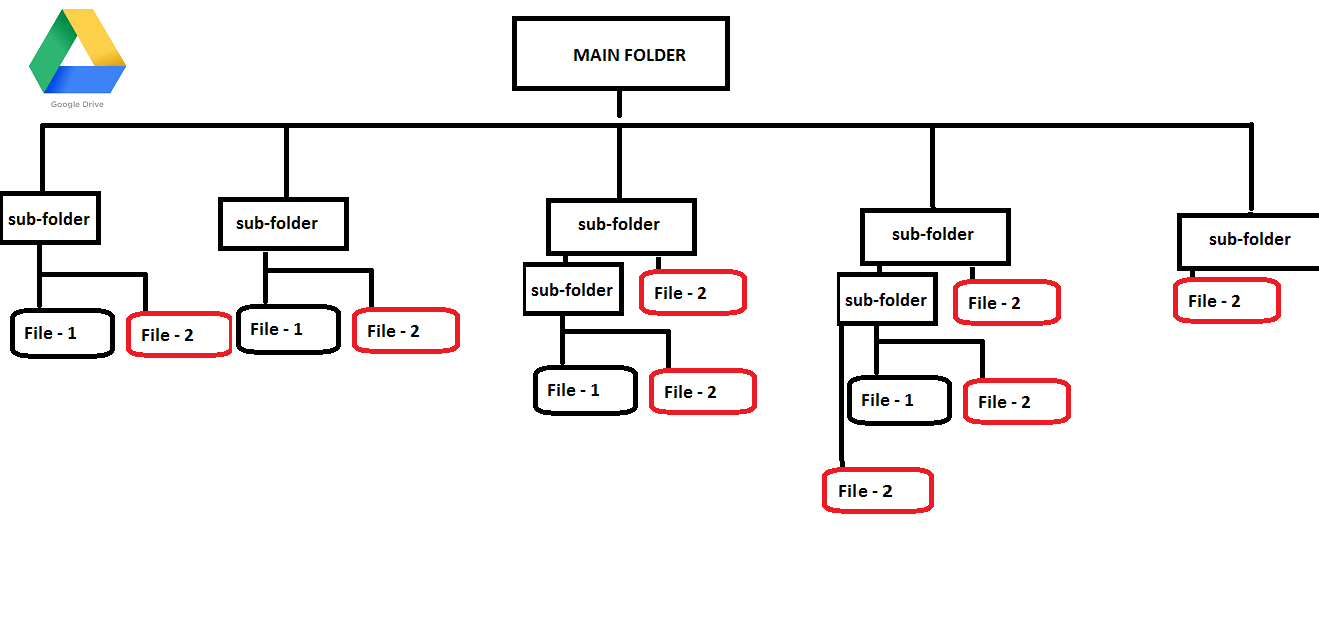
https://i.stack.imgur.com/hVXMa.png
Figure 2 – A hierarchical structure example
Why use it?
Using Google Drive will allow us the storage of a huge range of supported file sizes and formats, from music to videos, in addition to the most differentiated text and presentation formats, such as portfolios, for example.
Practical Activity
Purpose:
Use cloud storage to help the students understand how this resource can be used to create an open or closed digital repository, in a collaborative way without indexing.
Task Overview:
At the beginning of the lesson, the teacher shows that the creation of a repository using cloud storage follows a hierarchical structure of folders that will simplify the search for items. Afterwards, it explains the concept of cloud storage and how it can be used to create a digital repository without indexing. Next, it is given a task for the students to create a folder structure in the cloud and then they have to search for an image that should be placed in the respective folder (or subfolder) and define what type of repository should be created (open or closed).
Target students: 13-18 years old
Time: 120’
Materials and Resources: PC, tablets, smartphones and others; digital tool: Google Drive/ One drive or other cloud storage.

https://images.wondershare.com/drfone/article/2020/08/how-to-upload-pdf-to-google-drive-1.jpg
Figure 3 – Example of different formats supported by Drive
Exploring the task in the classroom:
At the beginning of the lesson, and using the chosen cloud storage system, the teacher explains what the creation of a folder and a subfolder consist of. The teacher should also take advantage of this moment to show how to send a document to one of the folders created earlier.
In a second phase, the teacher explains what type of sharing can be carried out with the folders so that users can collaborate in the creation of the repository and at the same time what type of public can collaborate in updating it.
The teacher structures a computer system so that the students can create their structure.
Hierarchical structure of a computer system
Information system
Devices
input devices
output Devices
input and Output Devices
storage devices
removable
fixed
Memoirs
primaries
secondary
Other Components
motherboard
processor
power supply
The teacher uses the structure of a computer system (or another that fits the final objective) so that the students can create their structure. Taking into account the number of students in the class, the teacher creates groups of 3 students so that they can create the folder structure in the cloud and later search for an image for each of the components of a computer system. That image must be placed in the respective folder (or subfolder). Students must also define what type of repository should be created (open or closed). Students must organize themselves in order to create the desired structure and place the respective images in the appropriate folder.
Assessment
The assessment can be done through direct assessment of the work done by students, as it allows the teacher to check students’ progress at a given stage, gather information about their strengths, needs and attitudes and assess their knowledge and skills.
Glossary
Cloud is a term used to describe a global network of servers, each with a unique function. The cloud is not a physical entity, but a vast network of remote servers around the world that are interconnected and that must function as a single ecosystem.

 English
English Português
Português Italiano
Italiano Macedonia
Macedonia Polski
Polski